The energy efficiency ratio (EER) is used for comparing the efficiency of different air conditioning systems or units. The EER of an air-conditioning system or unit is derived by dividing its cooling capacity by its electric power. Both metrics can be found on the device label. Cooling capacity is measured in British thermal units (BTU). The higher the EER, the more cooling capacity an air conditioner will produce per watt of electricity consumed and the more efficient it is. The EER should be indicated on the label or in the equipment datasheets.
Energy efficiency ratio (EER) = British thermal units (BTU) ÷ electric power of unit in watts (W).
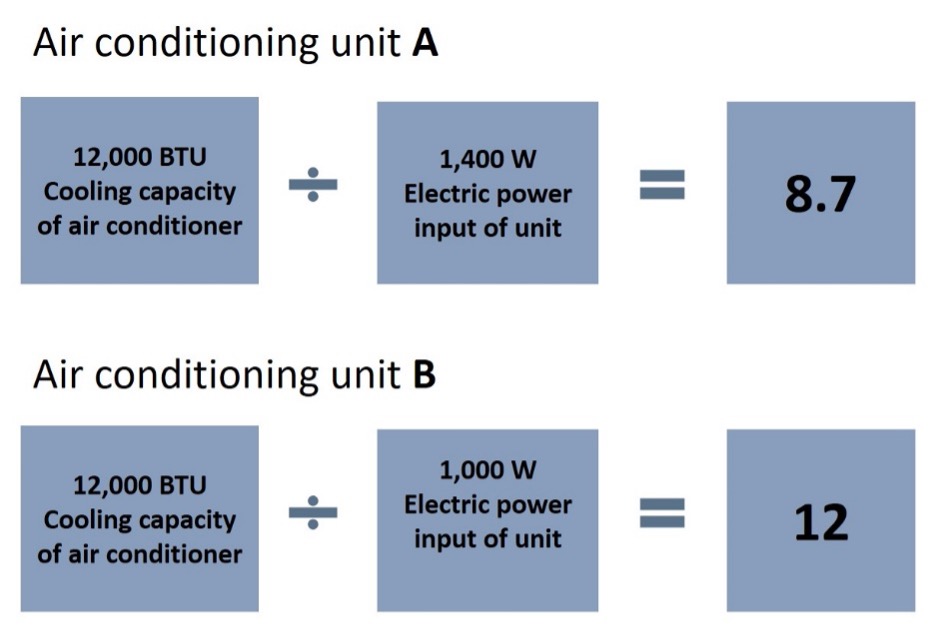
Two air conditioning units compared. Unit A has an EER of 8.7 (approx.); it produces 8.7 BTU of cooling capacity for every watt of electricity it consumes. Unit B has an EER of 12; it produces 12 BTU of cooling capacity for every watt of electricity it consumes. Unit B consumes nearly 30% less electricity than unit A, and will cost about 30% less to operate.
How much cooling capacity is required by a building or a room depends on the climate and the building. Well insulated buildings and those with passive cooling features will require less. Calculating cooling requirements is complex. Expert advice should be sought for this, as well as for the selection of an optimum air conditioning system.
Another ratio used is the seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER), which is the cooling output during a typical cooling season divided by the total electric energy input during the same period.
One BTU equals about 1,055 joules (J) or 0.29 watt-hours (Wh) or 0.00029 kilowatt hours (kWh).
