Offsetting the electricity consumption of a building means that instead buying all the electricity needed from the grid, a grid-connected PV system is installed to cover part of the electricity needs. However, such a system can usually not provide all of the electricity needed. For instance, this is the case at night or when the solar irradiation levels are insufficient.
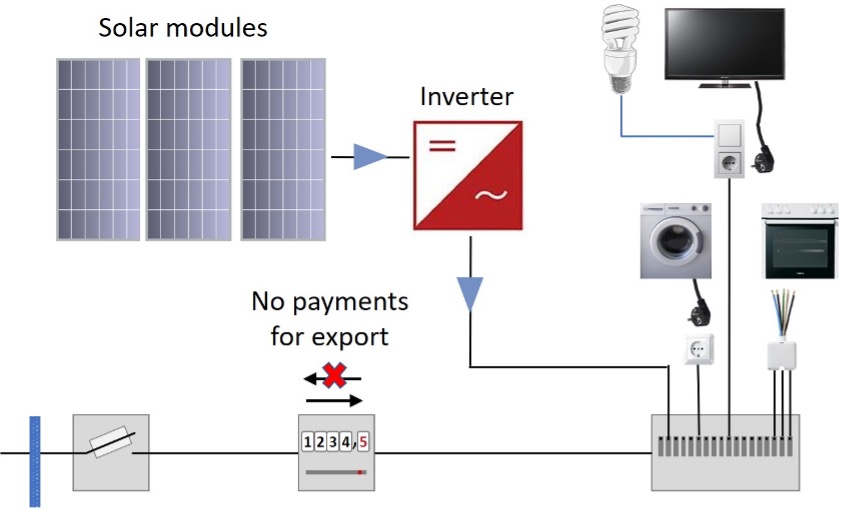
Metering configuration for offsetting electricity consumption. Meter stops running when solar is producing enough power for the building. Other configurations are possible.
Offsetting is similar to net metering except that there are no payments for any electricity exported to the grid. The PV module array should therefore be sized so that it does not produce more electricity than is needed.
Offsetting makes sense when the cost of electricity per kWh produced by the system is less than the cost of a kWh purchased from the grid and most electricity is consumed during the day. However, a system can also be sized to cover constant daytime loads, such as cooling fans or other equipment.
The meter must be suitable. Some meters can register electricity exported as electricity consumed, and add it to the electricity bill. Inverters with a ‘zero export’ function are available to ensure that no electricity is exported (which might not be permitted by some utilities).

pastillas priligy en mexico RSPC can provide greater accuracy in the assessment of distant recurrence risk when RS and pathology and clinical measures are discordant
agxz81