There are two types of electricity:
- Alternating current (AC) electricity, in which the direction of the electric current changes 50 or 60 times a second. AC electricity is delivered by the national electricity grid, diesel generators and inverters.
- Direct current (DC) electricity, in which the direction of the electric current does not change. DC electricity is delivered by photovoltaic modules and batteries.
An inverter converts DC electricity to AC electricity. Most appliances run on AC electricity.
Most solar PV systems have inverters, either to convert DC electricity from the PV modules into AC electricity, or to convert DC electricity from batteries into AC electricity.
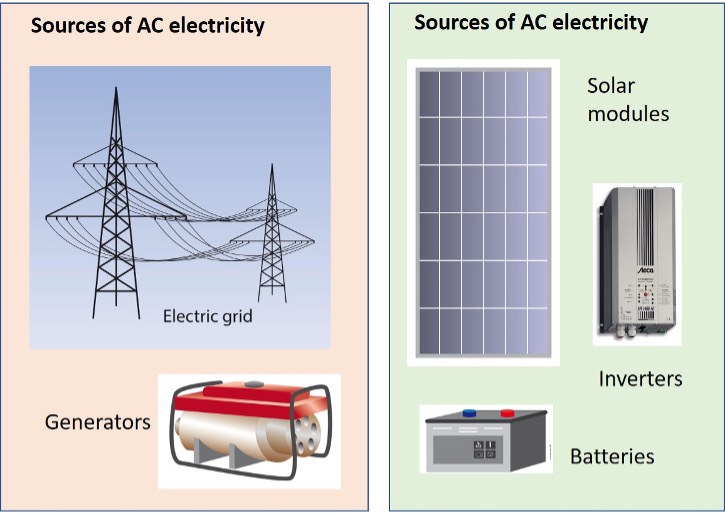
Sources of alternating current (AC) electricity and direct current (DC) electricity.

Symbols for alternating current (AC) electricity (left), direct current (DC) electricity (centre), and an inverter (right).

Salurin Syrup may interact with the following drugs and products priligy tablets price Nancy, you are right about the menopause confusion
tqvnqz