A lumen (lm) is the unit used to measure the total quantity of light emitted by a light source. The efficacy of a lamp is measured in lumens per watt (lm/W), i.e. the quantity of light emitted per watt of electricity consumed. The higher the lumens per watt (lm/W) of a lamp, the less electricity it will consume to produce a lumen of light.
When assessing a lamp, one needs to check the specifications. In general, the larger the lamp of a particular type is, the higher the efficacy will be. Another factor to take into consideration is the average service lives of different lighting technologies.
Automatic lighting control and light sensor equipment can result in significant savings by:
- Switching off lights when nobody is in a room (presence/motion sensors)
- Switching off lights when sufficient natural light is available (light sensors)
- Dimming lights when some natural light is available (light sensors, dimmers)
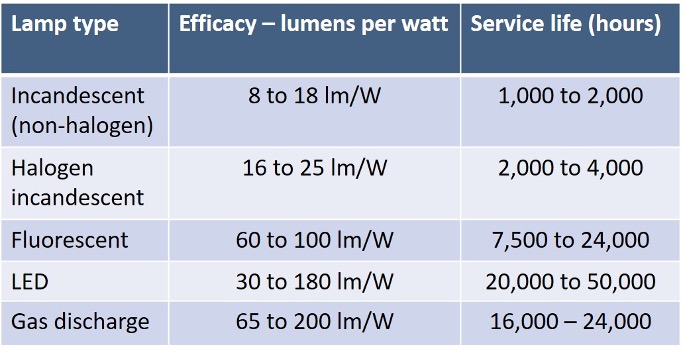
The approximate efficacy of different general purpose lighting technologies.
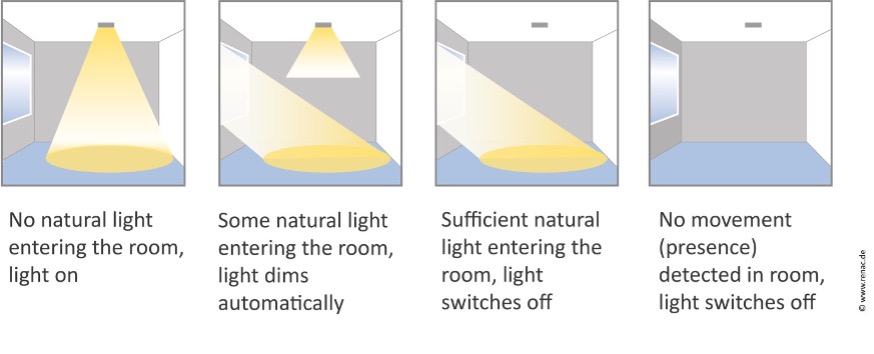
Automatic light sensor and control system.

Energy savings from a light sensor system.
Good lighting design practices (correct illuminations levels, installing lights in optimum locations, avoiding over illumination) can also reduce energy consumption. When implementing large projects, hiring a lighting engineer is recommended.
In office buildings, where lighting can account for more than half of the electricity consumption, considerable savings can be made. Having switches so that each lamp can be individually switched on and off, or dimmed, can also reduce energy consumption.

can you buy priligy in usa The best way to make sure you re getting the proper treatment is to act fast if you notice changes in your body
udgrbu