Electric drive systems convert electric energy into mechanical energy. They consist of an electric motor, a control system and a transmission system, such as a gearbox, which transfers the mechanical power of the electric motor to the working machine. Electric drives are used in pumps, cooling compressors, fans and compressors as well as material handling and processing equipment.
In the construction, industrial, transport and agriculture sectors, electric drives account for 53% of global final electricity consumption and over 70% of total industrial electricity consumption. It has been estimated that the implementation of energy efficiency improvements could reduce the worldwide electricity demand of electric motors by between 20% to 40% by 2040 compared to 2014.
Buying new machinery and replacing old machinery with more efficient machinery is a great opportunity to make economic savings.
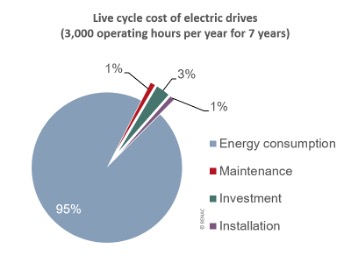
Life cycle costs of electric drives at 3,000 annual operating hours over a service life of 7 years. Up to 95% of the costs are derived from the electricity used.
The greatest savings potential lies in optimising mechanical systems, followed by more efficient end-use devices, the installation of variable speed drives, adopting the use of electronic speed controls and the use of highly efficient motors.
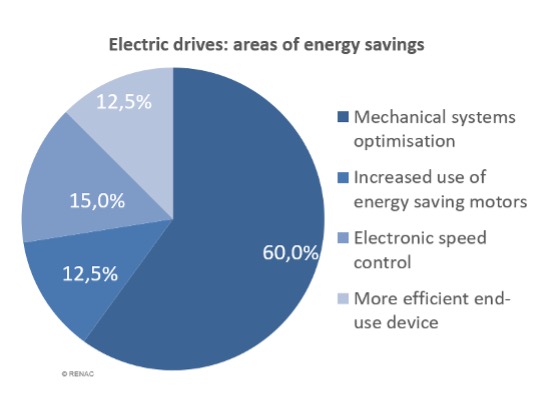
Potential areas of saving regarding electric drives.
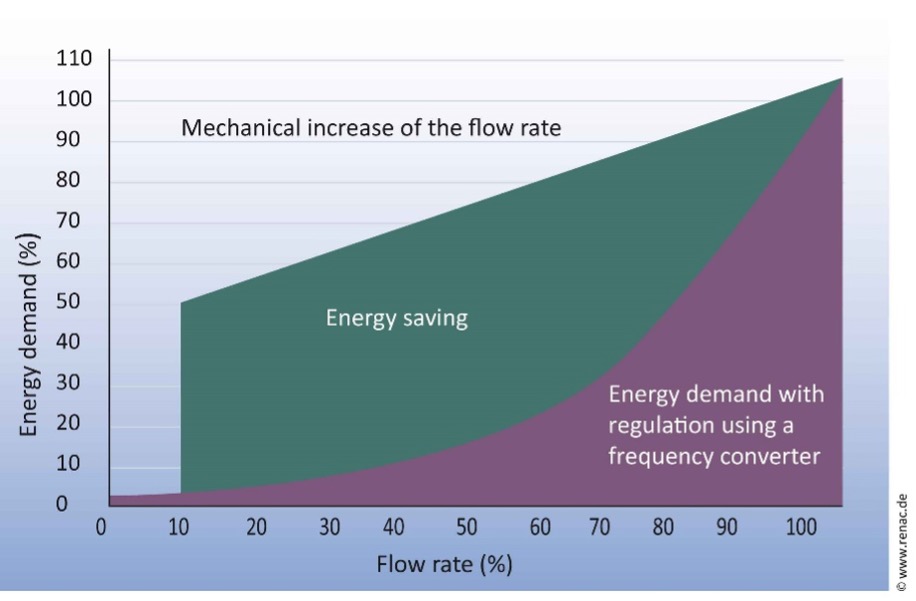
High energy savings can be achieved in the partial load range of electric drives, as illustrated in this example for an electrically driven pump.
Energy savings can also be made by optimising production processes, by removing energy-intensive steps and by improving operational control.
The payback periods for investments in energy efficiency measures related to electric drives are often only a few years.

Transdermal progesterone cream for vasomotor symptoms and postmenopausal bone loss order priligy online usa