Net metering is a type of metering for grid-connected systems.
Typically, only one kilowatt-hour meter is used, a two-way meter. This runs forwards when power is consumed from the grid and backwards when power is injected into the grid, or the meter has an import-export display. One kWh of PV power consumed means one less kWh that needs to be imported from the grid, thereby saving the system owner the cost of one kWh from the grid. The money saved by generating one kWh of PV electricity and the cost paid for one kWh of grid electricity are equal. In some schemes, system owners are not paid for any excess electricity they produce over and above their annual or monthly consumption; in other schemes they are paid for this excess power.
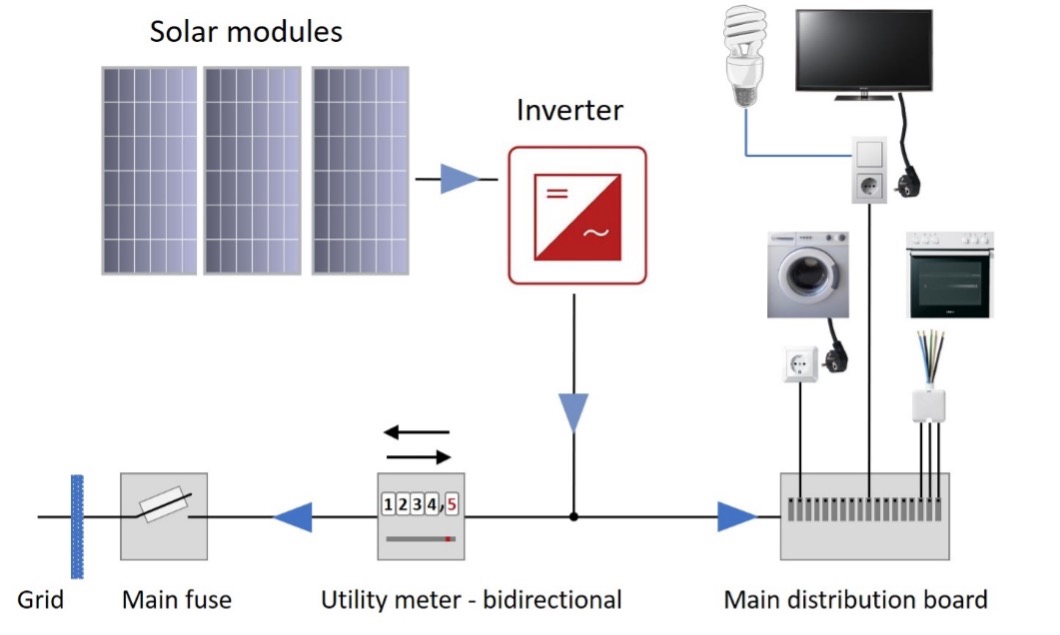
Net metering occurs when electricity is exported only when an excess is being produced by the PV modules. Other configurations are possible.
Net metering makes sense in situations where the cost of generating PV electricity is lower than buying it from the public grid (e.g. where tariffs during midday may be higher than during other times of the day).

priligy 30mg price 201490868 145
ojhsdl