Battery inverters (sometimes called unidirectional) are the most basic and the most common type of inverter used in off-grid PV systems. They are connected directly to the battery or battery bank and provide AC power for electrical AC appliances.
Power output is usually rated in watts (W). For example, a 200 W inverter will provide 200 W of electric power. They are available for different battery voltages, for example 12 V DC and 24 V DC.
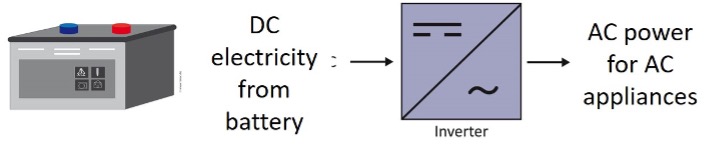
Battery inverters convert DC electric from batteries to AC electricity to power AC appliances.
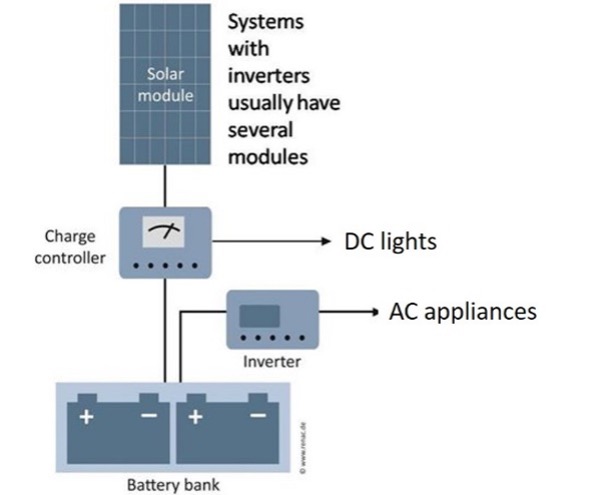
Example of a battery inverter in a small off-grid solar electric system. Battery voltage decreases as the battery discharges. The inverter will automatically switch off if it detects a very low battery voltage. However, this cut-off voltage is usually too low to protect the batteries. This complicates the use of inverters in off-grid PV systems. The system either has to be carefully managed by the system owner or an automatic solution must be implemented to protect the batteries. Having DC lights in the system can act as a warning mechanism – the charge controller will disconnect the DC lights before the battery discharges to such an extent that it may be damaged, and allow time for the battery to recharge again.
Battery inverters are very common and most are not specifically designed for use in solar systems. It is recommended that inverters that are to be used in solar systems be purchased from companies which supply equipment specifically for PV systems as these inverters will be more efficient and have longer service lives.
Some battery inverters designed for use with PV systems have integrated solar charge controllers.
