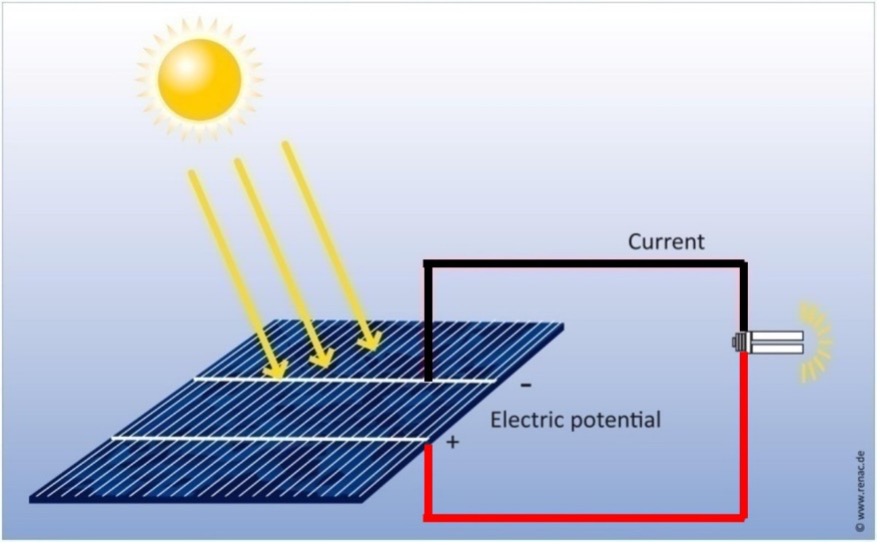
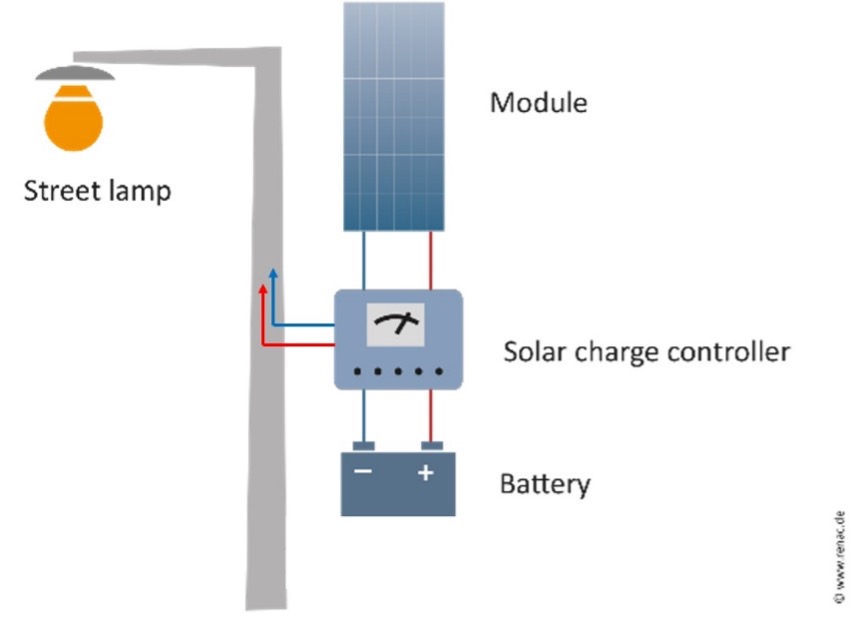
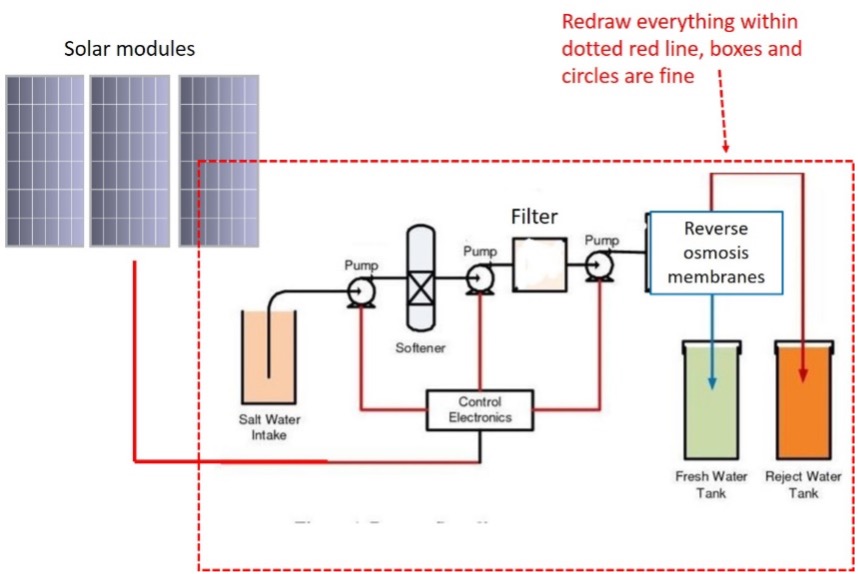
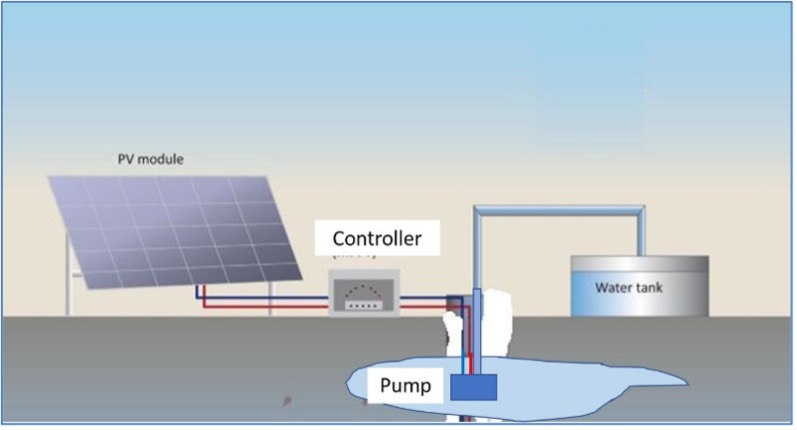
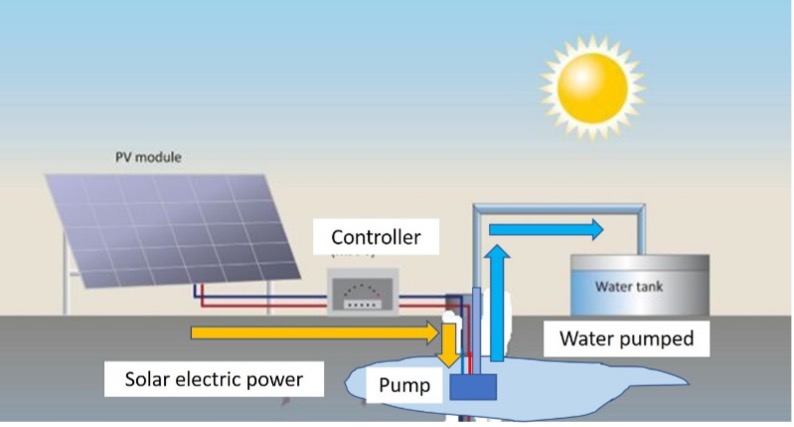
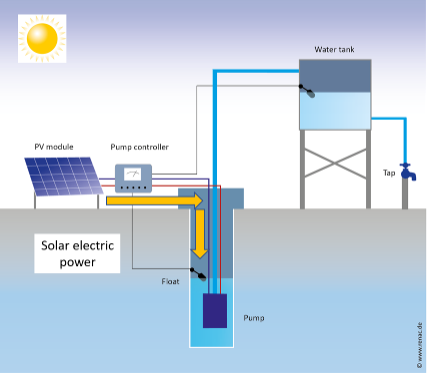
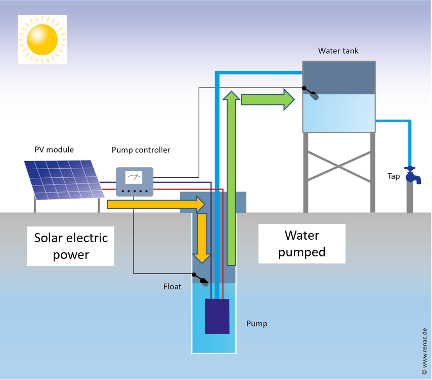
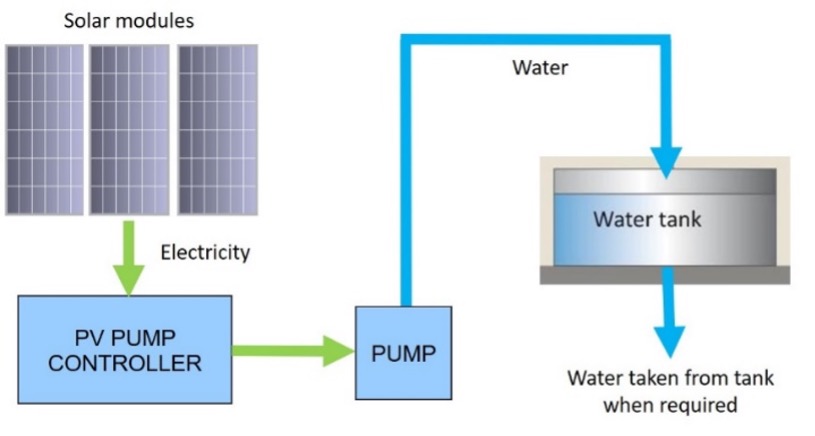
The main types of PV module technologies, about 95% of the global market, are:
- Monocrystalline silicon modules
- Polycrystalline silicon modules
Polycrystalline silicon modules are slightly less efficient than monocrystalline silicon modules. This means that polycrystalline silicon modules take up more surface area on a roof or require a larger mounting structure than monocrystalline silicon modules to produce the same amount of electricity.
Both types are manufactured to high international standards and are suitable for most applications. Typical warranties guarantee that after 20/25 years of use, the modules will produce 80% of their original rated power output.
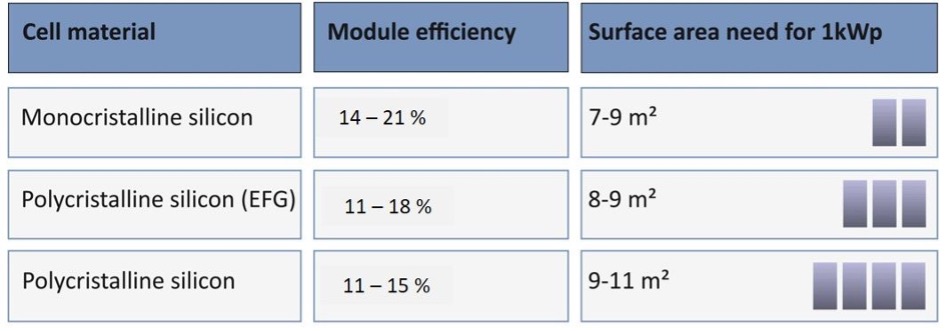
Approximate comparison of the efficiencies of different crystalline silicon PV modules, and the surface area needed for 1 kWp of PV module array. Lower efficiency requires a larger module surface area to achieve the same total power output. EFG polycrystalline modules are the more efficient type of polycrystalline module.
PERC (passivated emitter and rear contact) PV modules are a more efficient type of mono crystalline PV technology. Other technologies include thin film photovoltaics, where photovoltaic active semiconductor compounds like cadmium telluride are sputtered on flat glass. Lower efficiencies and high degradation have prevented thin film PV from gaining significant market share.