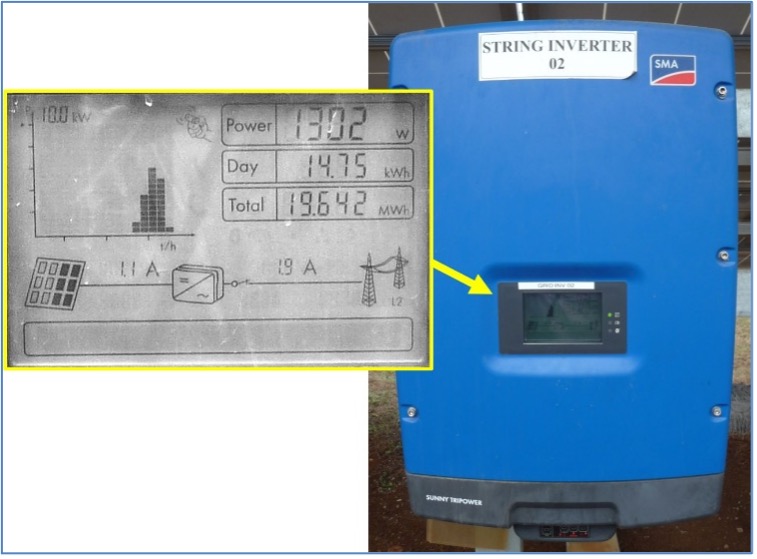
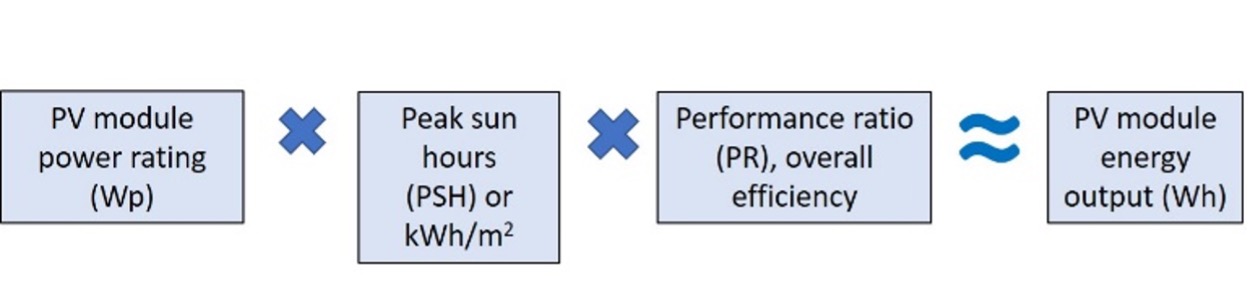
The efficiency (ƞ) of a machine or electrical appliance is ratio of the useful work produced by the machine or the electrical appliance to the energy consumed by the machine.
efficiency (ƞ) = Output/input.
Efficiency ƞ (%) = (energy output in watts ÷ energy input in watts) x 100.
The energy wasted (losses) during the process is usually in the form of heat.
Energy efficiency refers to using less energy (input) to provide the same result and perform the same task (output).

All engines, machines and electrical appliances have energy losses. The fewer the losses, the more efficient the energy use
A simple example is to compare two lamps, a non-halogen incandescent lamp (old type) and a fluorescent lamp, both providing the same level of illumination. The incandescent lamp wastes 90% of the energy it consumes as heat, while the fluorescent lamp wastes only 25% as heat. Thus, the fluorescent lamp consumes about 85% less energy than the incandescent lamp while providing the same level of illumination.
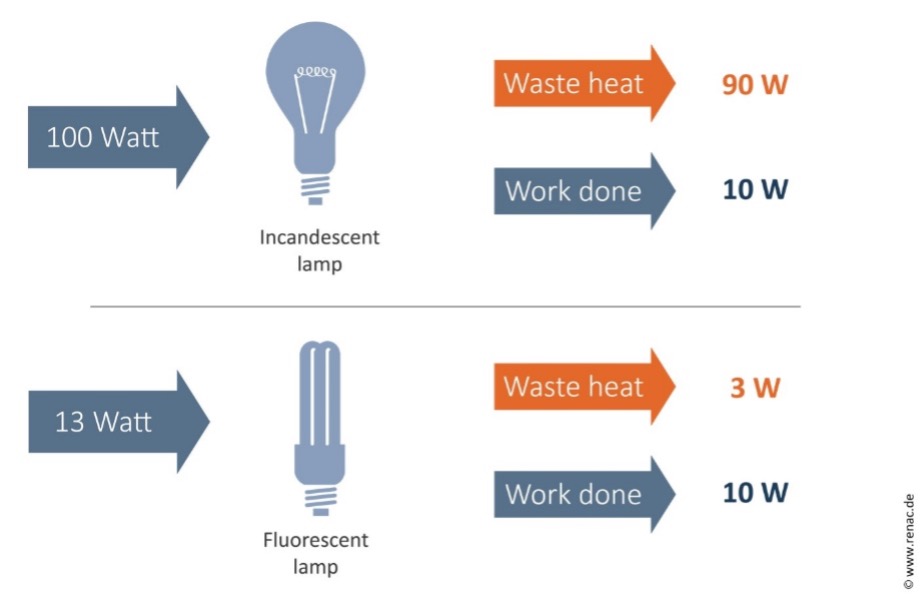
Energy efficiency / energy losses, comparing incandescent lighting with fluorescent lighting.
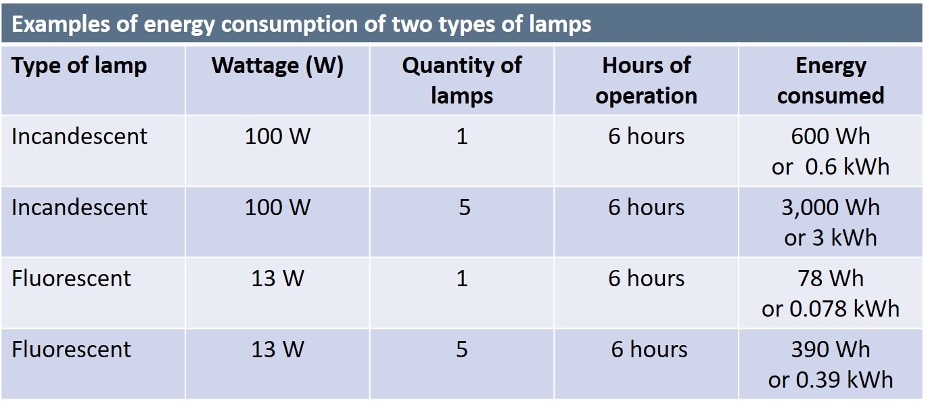
Energy efficiency, comparing lamps. Energy consumed = lamp wattage x quantity of lamps x hours of operation.
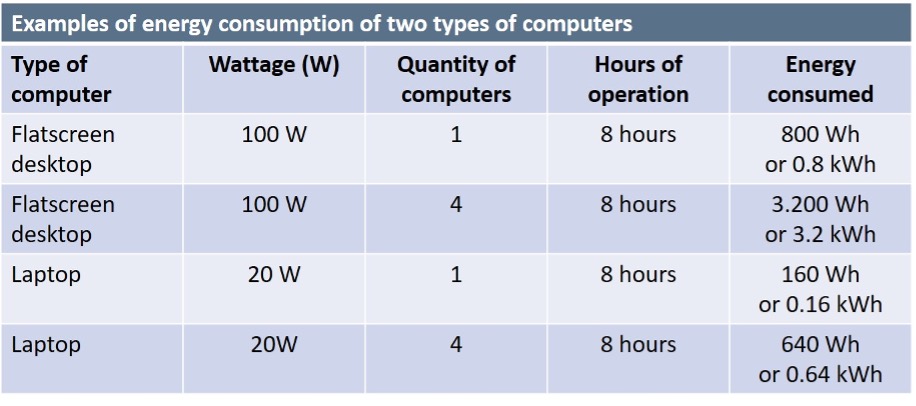
Energy efficiency, comparing computers. Energy consumed = computer wattage x quantity of computers x hours of operation.
The above or only examples for demonstration purposes. The same basic principles apply to non-electrical equipment.