Air conditioning uses a lot of energy. The cost of operating an air-conditioning system or unit over its service life is many times the cost of the equipment.

Air conditioning uses over 10% of all electricity produced globally.
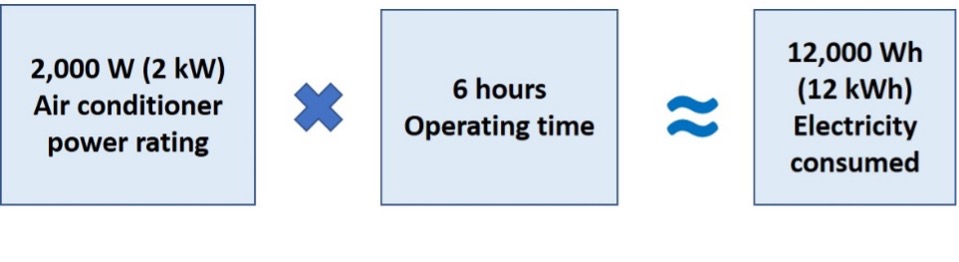
Electricity consumption of a 2,000 W air-conditioning unit which is on for 6 hours 2,000 W x 6 hours ≈ 12,000 Wh or 12 kWh. Over a week this is 12 kWh x 7 days ≈ 84 kWh.
Opportunities to save energy used for cooling include:
- Operating systems more efficiently.
- Using more efficient systems.
- Alternative cooling technologies.
- Passive cooling of buildings.
Individual units enable a better control of the temperature in individual rooms, reducing overall energy consumption.
Inverter air conditioners – unlike conventional air conditioners, which regulate temperature by switching on and off – operate at variable speeds, using only the amount of energy required to maintain the required temperature, consuming less energy than conventional units. However, their initial investment costs are higher.
Solar air conditioners are available which are powered partially or totally by solar energy.
Fans create a wind chill effect and consume only a fraction of the energy of air conditioners, and should be used where appropriate.
With new buildings and renovations, the cooling requirements of buildings can be significantly reduced by employing passive cooling techniques such as insulation, shading, windows with heat-reflecting glass and other features.