Often, electricity purchased from the utility is charged at a higher tariff when electricity consumption goes above a certain level. When it is below this level, the standard tariff is charged. A grid-connected PV system can be sized to produce enough electricity to ensure that electricity consumption never goes above the level at which peak tariffs are charged. The size of the PV system will depend on the electricity demand profile, solar irradiation and tariff arrangements. A net-metering arrangement would normally be used.

Graphical representation of sample electricity consumption during the day where a peak tariff is charged when electricity consumption exceeds a certain amount
In situations where daytime electricity prices are higher than at other times, a grid-connected PV system can be used to replace this expensive grid electricity with electricity generated by a grid-connected PV system.
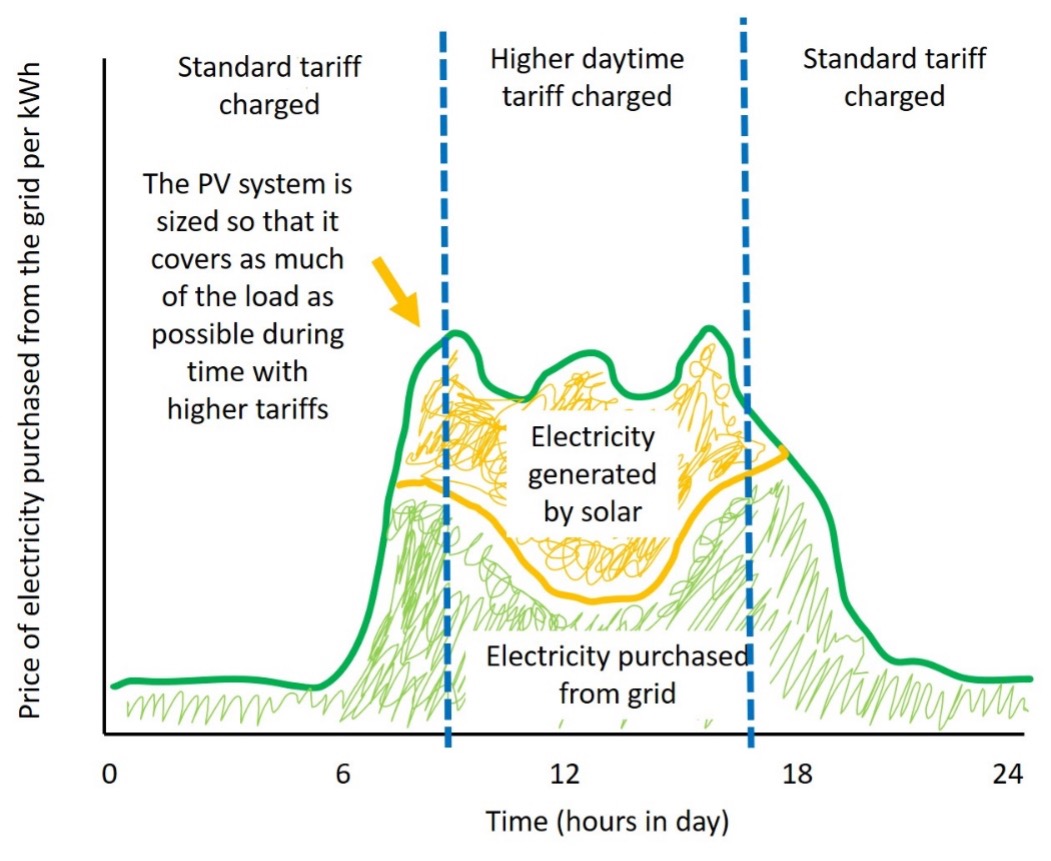
Most of the solar electricity is generated during the time period when electricity from the grid is most expensive. The size of the PV system will depend on the load profile, solar irradiation, and tariff arrangements. A net-metering arrangement would normally be used.
Utility tariff structures can be complex. For example, in addition to a higher tariff above a certain level of electricity consumption, the cost of electricity per kWh could also differ at different times during the day. Therefore, a clear understanding of utility tariff arrangements is required so that the PV system delivers optimum cost savings and does not produce more electricity than is required.
Peak daytime electricity can also be reduced by the use of low-energy and energy-efficient electrical appliances, and replacing electric water heating with a solar water heating system.
